EAB Treatment Program

The emerald ash borer (EAB) has become one of the most destructive non-native forest pests in U.S. history. This beetle was first detected in Michigan in 2002. By 2018 it had spread to at least 32 states and 4 Canadian provinces, killing millions of ash trees and likely causing over $10 billion of damage.
While beetle populations have been difficult to control, insecticidal treatments can protect individual trees from beetle damage for a period of 2-3 years.
Emerald ash borer has been present in Virginia since at least 2012. It has now been detected in more than half of Virginia counties and continues to spread. In response, the Virginia Department of Forestry developed a cost-sharing program called the Emerald Ash Borer Treatment Program (EABTP), which began in January 2018. The purpose of this program is to preserve remnant populations of ash trees around the state, and to promote protection of ash trees among Virginia municipalities, organizations and property owners.
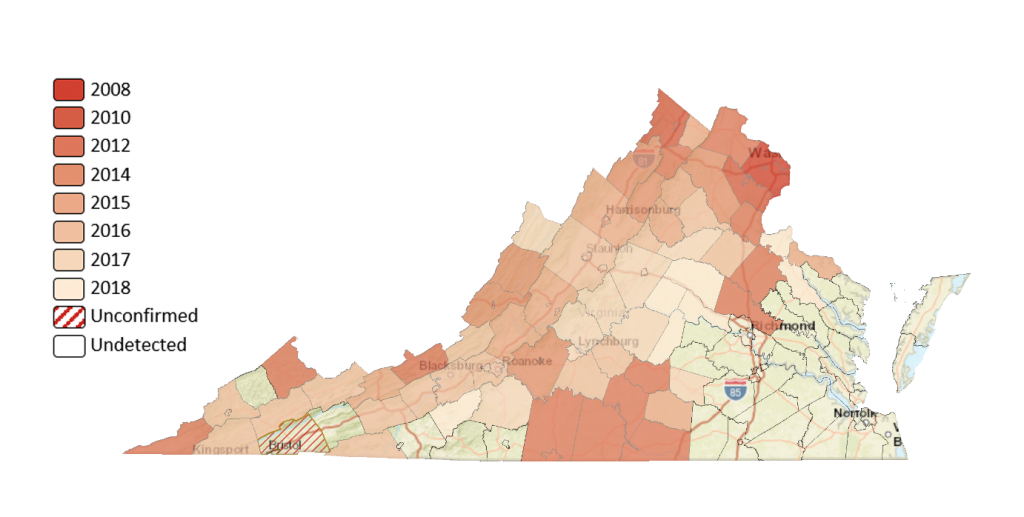 Year of EAB first detection in Virginia counties
Year of EAB first detection in Virginia counties
Virginia Department of Forestry (VDOF) accepted applications for the first year of the EABTP from January until June of 2018. A complete application required a written plan for future ash protection, an on-site approval of a VDOF forester, and a quote for insecticidal treatment from a licensed pesticide applicator, typically an arborist. Approved municipalities, organizations, and private property owners received up to half the cost of insecticidal treatment of ash trees.
A total of 122 organizations and individuals completed applications for funding in the first year of the EABTP . About 85% of applicants were homeowners.
For more information on the emerald ash borer in North America, see emeraldashborer.info.